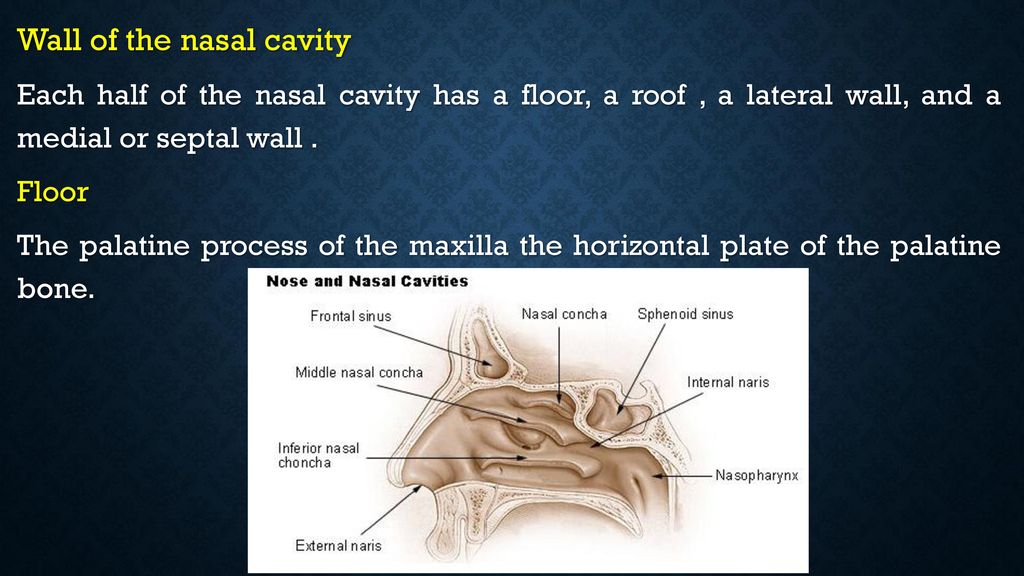
Formed by the roof of the mouth the floor of the nasal cavity consists of the soft palate behind and the hard palate in front.
What is the floor of the nasal cavity called.
The floor of the nasal cavity is read more.
Thus the crack through which the above sinuses drain is called the.
The nasal cavity is separated in the middle by the nasal septum which also forms the medial wall of each half of the cavity.
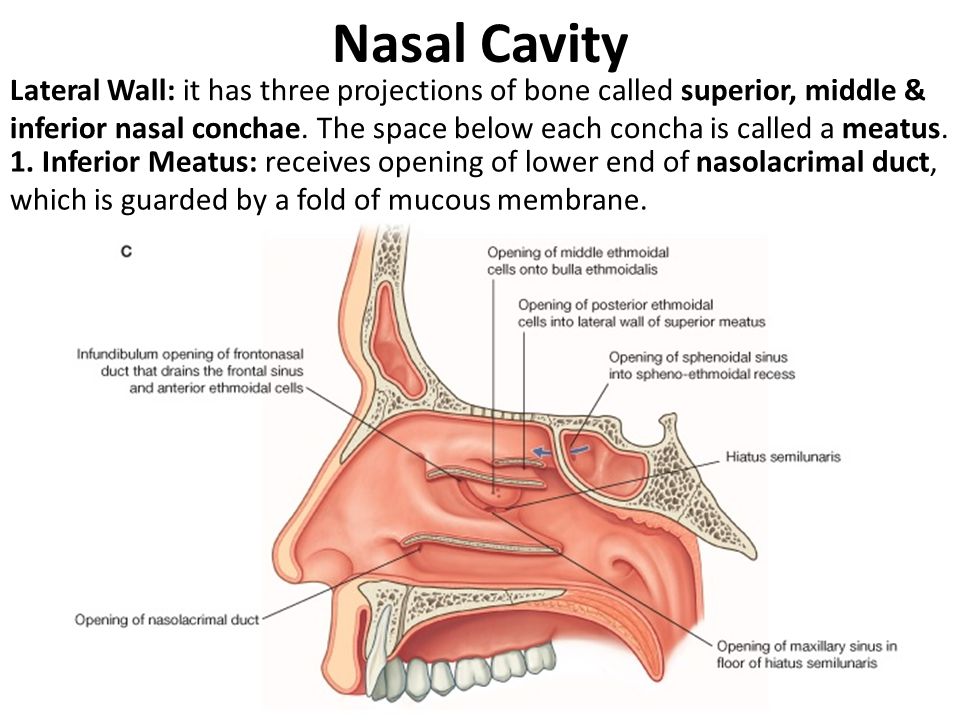
The inferior meatus drainage from that channels from to nasal cavity.
The floor of the nasal cavity is formed by the hard palate on the roof of the mouth while the walls have folded sections called turbinates which serve to increase the surface area.
There are six walls forming the borders of the bony nasal cavity.
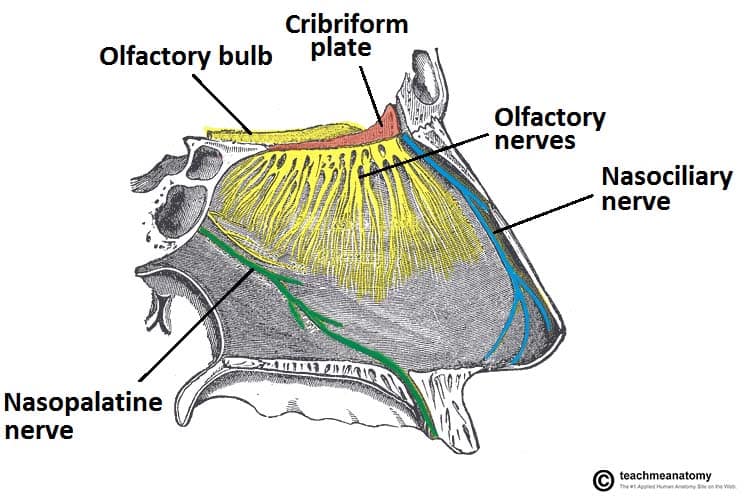
Because of its position in the skull there is one bone that forms part of the floor of the cranium the roof of the nasal cavity a wall of the eye orbit and divides the nasal cavity into two parts.
The horizontal plate of the palatine bone posteriorly and the palatine process of the maxilla anteriorly.
While the soft palate is composed of involuntary muscle the hard palate consists of the maxilla and the palatine bones.
The ethmoidal bullae is protrusion of the that functions to.
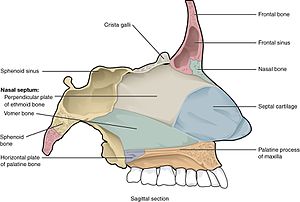
The nasal septum is composed of cartilage and bone.
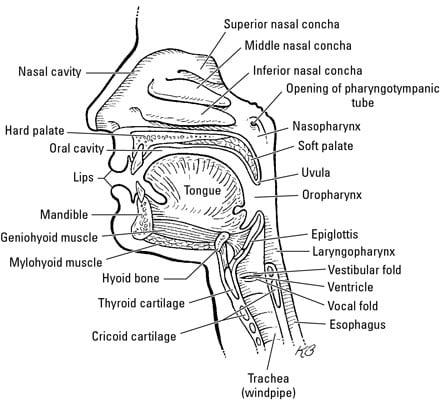
Nasal cavity the cavity on either side of the nasal septum extending from the nares to the pharynx and lying between the floor of the cranium and the roof of the mouth.
The floor of the nasal cavities which also form the roof of the mouth is made up by the bones of the hard palate.
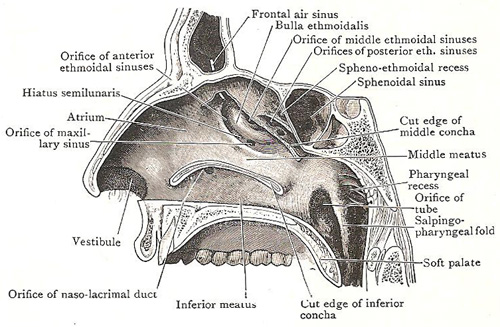
A number of paranasal air sinuses empty into this space including.
It makes up the upper respiratory system along with the paranasal sinuses oral cavity pharynx and larynx 2 and is the.
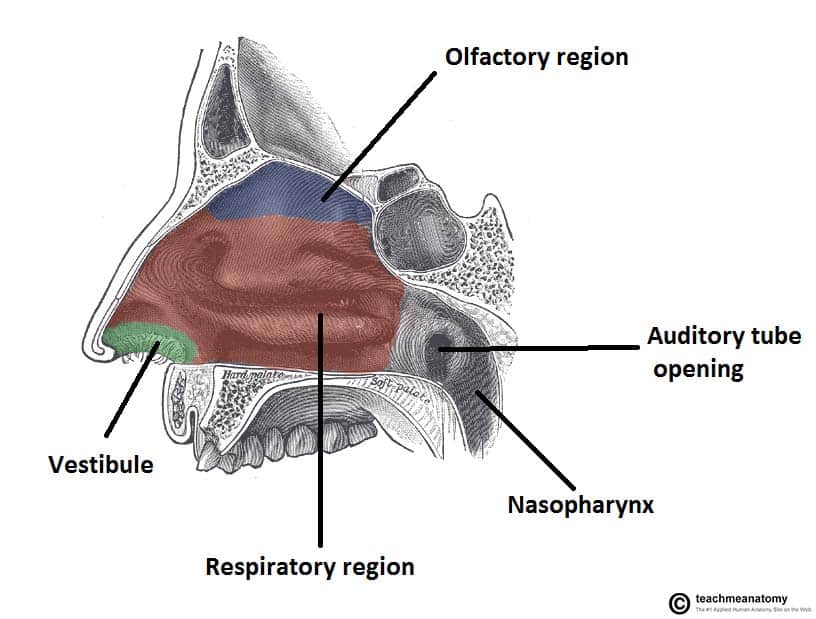
The most anterior part of the nasal cavity is the nasal vestibule.
Each canal opens to the face by a nostril and into the pharynx by the choana.
Paranasal sinus drainage 1.
Of an internal space the nasal cavity.
Posteriorly the nasal cavity opens into the nasopharynx through a pair of oval openings called the choanae.
Besides the anterior and posterior apertures each nasal cavity has a roof floor and lateral and medial walls there are 12 cranial bones in total that contribute to the nasal cavity structure which include the paired nasal maxilla palatine and lacrimal bones as well as the unpaired ethmoid sphenoid frontal and vomer bones among all of them the ethmoid bone is the most important.
It is subdivided into a left and right canal by a thin medial cartilaginous and bony wall the nasal septum.
If the septum is enlarged or deviated it may block the airflow.







:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10814/Nose.png)